agent在环境environment中学习,根据环境的状态state(或观测到的observation),执行动作action,并根据环境的反馈reward(奖励)来指导更好的动作。比如本项目的Cart pole小游戏中,agent就是动图中的杆子,杆子有向左向右两种action。
## 安装依赖!pip install pygame !pip install gym !pip install atari_py !pip install parl
import gymimport osimport randomimport collectionsimport paddleimport paddle.nn as nnimport numpy as npimport paddle.nn.functional as F
经验回放主要做的事情是:把结果存入经验池,然后经验池中随机取出一条结果进行训练。
这样做有两个好处:
之所以加入experience replay是因为样本是从游戏中的连续帧获得的,这与简单的reinforcement learning问题相比,样本的关联性大了很多,如果没有experience replay,算法在连续一段时间内基本朝着同一个方向做gradient descent,那么同样的步长下这样直接计算gradient就有可能不收敛。因此experience replay是从一个memory pool中随机选取了一些expeirence,然后再求梯度,从而避免了这个问题。
class ReplayMemory(object):def __init__(self, max_size):self.buffer = collections.deque(maxlen=max_size)# 增加一条经验到经验池中def append(self, exp):self.buffer.append(exp)# 从经验池中选取N条经验出来def sample(self, batch_size):mini_batch = random.sample(self.buffer, batch_size)obs_batch, action_batch, reward_batch, next_obs_batch, done_batch = [], [], [], [], []for experience in mini_batch:s, a, r, s_p, done = experience
obs_batch.append(s)action_batch.append(a)reward_batch.append(r)next_obs_batch.append(s_p)done_batch.append(done)return np.array(obs_batch).astype('float32'), np.array(action_batch).astype('float32'), np.array(reward_batch).astype('float32'), np.array(next_obs_batch).astype('float32'), np.array(done_batch).astype('float32')def __len__(self):return len(self.buffer)DQN算法较普通算法在经验回放和固定Q目标有了较大的改进,主要原因:
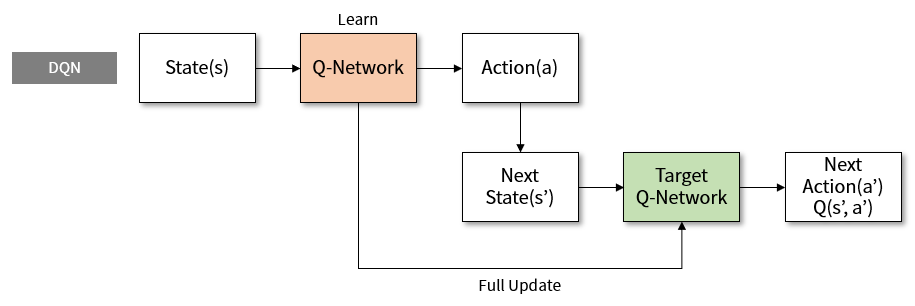
这里的模型可以根据自己的需求选择不同的神经网络组建。
DQN用来定义前向(Forward)网络,可以自由的定制自己的网络结构。
class DQN(nn.Layer):def __init__(self, outputs):super(DQN, self).__init__()self.linear1 = nn.Linear(in_features=4, out_features=128)self.linear2 = nn.Linear(in_features=128, out_features=24)self.linear3 = nn.Linear(in_features=24, out_features=outputs)def forward(self, x):x = self.linear1(x)x = F.relu(x)x = self.linear2(x)x = F.relu(x)x = self.linear3(x)return x
这里包括模型探索与模型训练两个部分
Agent负责算法与环境的交互,在交互过程中把生成的数据提供给Algorithm来更新模型(Model),数据的预处理流程也一般定义在这里。
def sample(obs, MODEL):global E_GREEDglobal ACTION_DIMglobal E_GREED_DECREMENT
sample = np.random.rand() # 产生0~1之间的小数if sample < E_GREED:act = np.random.randint(ACTION_DIM) # 探索:每个动作都有概率被选择else:obs = np.expand_dims(obs, axis=0)obs = paddle.to_tensor(obs, dtype='float32')act = MODEL(obs)act = np.argmax(act.numpy()) # 选择最优动作E_GREED = max(0.01, E_GREED - E_GREED_DECREMENT) # 随着训练逐步收敛,探索的程度慢慢降低return actdef learn(obs, act, reward, next_obs, terminal, TARGET_MODEL, MODEL):global global_step# 每隔200个training steps同步一次model和target_model的参数if global_step % 50 == 0:TARGET_MODEL.load_dict(MODEL.state_dict())global_step += 1obs = np.array(obs).astype('float32')next_obs = np.array(next_obs).astype('float32')# act = np.expand_dims(act, -1)cost = optimize_model(obs, act, reward, next_obs, terminal, TARGET_MODEL, MODEL) # 训练一次网络return costdef optimize_model(obs, action, reward, next_obs, terminal, TARGET_MODEL, MODEL):""" 使用DQN算法更新self.model的value网络 """# 从target_model中获取 max Q' 的值,用于计算target_Qglobal E_GREEDglobal ACTION_DIMglobal E_GREED_DECREMENTglobal GAMMAglobal LEARNING_RATEglobal opt
opt = paddle.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate=LEARNING_RATE,parameters=MODEL.parameters()) # 优化器(动态图)obs = paddle.to_tensor(obs)next_obs = paddle.to_tensor(next_obs)next_pred_value = TARGET_MODEL(next_obs).detach()best_v = paddle.max(next_pred_value, axis=1)target = reward + (1.0 - terminal) * GAMMA * best_v.numpy()target = paddle.to_tensor(target)pred_value = MODEL(obs) # 获取Q预测值# 将action转onehot向量,比如:3 => [0,0,0,1,0]action = paddle.to_tensor(action.astype('int32'))action_onehot = F.one_hot(action, ACTION_DIM)action_onehot = paddle.cast(action_onehot, dtype='float32')# 下面一行是逐元素相乘,拿到action对应的 Q(s,a)pred_action_value = paddle.sum(paddle.multiply(action_onehot, pred_value), axis=1)# 计算 Q(s,a) 与 target_Q的均方差,得到losscost = F.square_error_cost(pred_action_value, target)cost = paddle.mean(cost)avg_cost = cost
cost.backward()opt.step()opt.clear_grad()return avg_cost.numpy()def run_train(env, rpm, TARGET_MODEL, MODEL):MODEL.train()TARGET_MODEL.train()total_reward = 0obs = env.reset()global global_stepwhile True:global_step += 1# 获取随机动作和执行游戏action = sample(obs, MODEL)next_obs, reward, isOver, info = env.step(action)# 记录数据rpm.append((obs, action, reward, next_obs, isOver))# 在预热完成之后,每隔LEARN_FREQ步数就训练一次if (len(rpm) > MEMORY_WARMUP_SIZE) and (global_step % LEARN_FREQ == 0):(batch_obs, batch_action, batch_reward, batch_next_obs, batch_isOver) = rpm.sample(BATCH_SIZE)train_loss = learn(batch_obs, batch_action, batch_reward, batch_next_obs, batch_isOver, TARGET_MODEL, MODEL)total_reward += reward
obs = next_obs.astype('float32')# 结束游戏if isOver:breakreturn total_rewarddef evaluate(model, env, render=False):model.eval()eval_reward = []for i in range(5):obs = env.reset()episode_reward = 0while True:obs = np.expand_dims(obs, axis=0)obs = paddle.to_tensor(obs, dtype='float32')action = model(obs)action = np.argmax(action.numpy())obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)episode_reward += rewardif render:env.render()if done:breakeval_reward.append(episode_reward)return np.mean(eval_reward)设置超参数
LEARN_FREQ = 5 # 训练频率,不需要每一个step都learn,攒一些新增经验后再learn,提高效率MEMORY_SIZE = 20000 # replay memory的大小,越大越占用内存MEMORY_WARMUP_SIZE = 200 # replay_memory 里需要预存一些经验数据,再开启训练BATCH_SIZE = 32 # 每次给agent learn的数据数量,从replay memory随机里sample一批数据出来LEARNING_RATE = 0.001 # 学习率大小GAMMA = 0.99 # reward 的衰减因子,一般取 0.9 到 0.999 不等E_GREED = 0.1 # 探索初始概率E_GREED_DECREMENT = 1e-6 # 在训练过程中,降低探索的概率MAX_EPISODE = 20000 # 训练次数SAVE_MODEL_PATH = "models/save" # 保存模型路径OBS_DIM = None ACTION_DIM = None global_step = 0
def main():global OBS_DIMglobal ACTION_DIM
train_step_list = []train_reward_list = []evaluate_step_list = []evaluate_reward_list = []# 初始化游戏env = gym.make('CartPole-v0')# 图像输入形状和动作维度action_dim = env.action_space.n
obs_dim = env.observation_space.shape
OBS_DIM = obs_dim
ACTION_DIM = action_dim
max_score = -int(1e4)# 创建存储执行游戏的内存rpm = ReplayMemory(MEMORY_SIZE)MODEL = DQN(ACTION_DIM)TARGET_MODEL = DQN(ACTION_DIM)# if os.path.exists(os.path.dirname(SAVE_MODEL_PATH)):# MODEL_DICT = paddle.load(SAVE_MODEL_PATH+'.pdparams')# MODEL.load_dict(MODEL_DICT) # 加载模型参数print("filling memory...")while len(rpm) < MEMORY_WARMUP_SIZE:run_train(env, rpm, TARGET_MODEL, MODEL)print("filling memory done")# 开始训练episode = 0print("start training...")# 训练max_episode个回合,test部分不计算入episode数量while episode < MAX_EPISODE:# train partfor i in range(0, int(50)):# First we need a statetotal_reward = run_train(env, rpm, TARGET_MODEL, MODEL)episode += 1# print("episode:{} reward:{}".format(episode, str(total_reward)))# test part# print("start evaluation...")eval_reward = evaluate(TARGET_MODEL, env)print('episode:{} e_greed:{} test_reward:{}'.format(episode, E_GREED, eval_reward))evaluate_step_list.append(episode)evaluate_reward_list.append(eval_reward)# if eval_reward > max_score or not os.path.exists(os.path.dirname(SAVE_MODEL_PATH)):# max_score = eval_reward# paddle.save(TARGET_MODEL.state_dict(), SAVE_MODEL_PATH+'.pdparams') # 保存模型if __name__ == '__main__':main()filling memory...
filling memory done
start training...
episode:50 e_greed:0.0992949999999993 test_reward:9.0
episode:100 e_greed:0.0987909999999988 test_reward:9.8
episode:150 e_greed:0.09827199999999828 test_reward:10.0
episode:200 e_greed:0.09777599999999778 test_reward:8.8
episode:250 e_greed:0.09726999999999728 test_reward:9.0
episode:300 e_greed:0.09676199999999677 test_reward:10.0
episode:350 e_greed:0.0961919999999962 test_reward:14.8
https://www.heywhale.com/mw/project/649e7d3f70567260f8f11d2b
更多优质内容请关注公号:汀丶人工智能
Copyright © 2023 leiyu.cn. All Rights Reserved. 磊宇云计算 版权所有 许可证编号:B1-20233142/B2-20230630 山东磊宇云计算有限公司 鲁ICP备2020045424号
磊宇云计算致力于以最 “绿色节能” 的方式,让每一位上云的客户成为全球绿色节能和降低碳排放的贡献者