功能:将数据进行链式储存
链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接实现的
链表的组成:
结点的组成:
STL中链表是一个双向循环列表
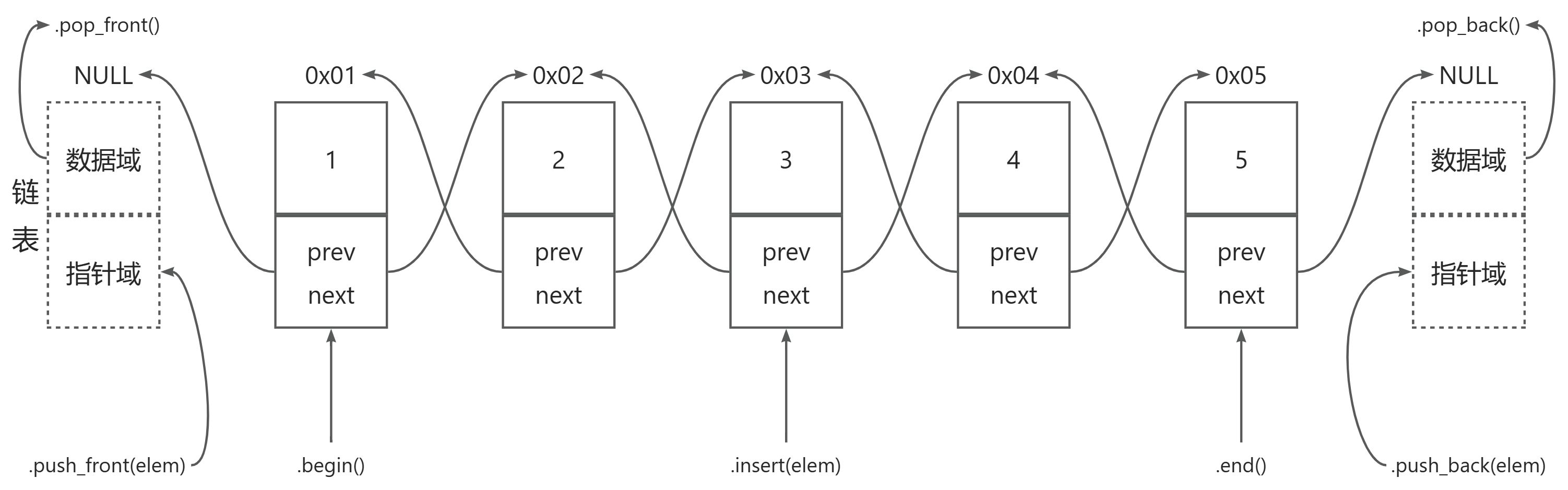
list的优点:
缺点:
list的重要性质:
STL中list和vector是最常被使用的容器,各有优缺点
listlst; //采用模板类实现,默认构造函数list(beg, end);//构造函数将[beg,end)区间中的元素拷贝给自身list(n, elem);//将n个elem拷贝给自身list(const list& list);//拷贝构造函数#include#includeusing namespace std; void PrintList(const list& lst) { for (list::const_iterator it = lst.begin(); it != lst.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; } cout << endl; } int main() { listL1;//默认构造 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { L1.push_back(i); } PrintList(L1); listL2(L1.begin(), L1.end());//区间方式构造 PrintList(L2); listL3(L2);//拷贝构造 PrintList(L3); listL4(10, 2);//n个elem PrintList(L4); return 0; }
.assign(beg, end);//将[beg,end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给自身.assign(n, elem);//将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身list& operator=(const list& lst);//重载等号运算符.swap(lst);//将lst与本身元素互换#include#includeusing namespace std; void PrintList(const list& lst) { for (list::const_iterator it = lst.begin(); it != lst.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; } cout << endl; } int main() { listL1;//默认构造 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { L1.push_back(i); } listL2; L2.assign(L1.begin(), L1.end());//区间赋值 PrintList(L2); L2.assign(10, 1);//n个elem赋值 PrintList(L2); L2 = L1;//等号赋值 PrintList(L2); return 0; }
.empty();//判断容器是否为空.size();//返回容器中元素的个数.resize(int num);//重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值0填充新位置;如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除.resize(int num, elem);//重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置;如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除两端插入操作:
.push_back(elem);//尾插.push_front(elem);//头插.pop_back();//尾删.pop_front();//头删指定位置操作:
.insert(pos, elem);//在pos位置插入elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置.insert(pos, n, elem);//在pos位置插入n个elem元素数据,无返回值.insert(pos, beg, end);//在pos位置插入[beg,end)区间的数据,无返回值.clear();//清空容器内所有数据.eraser(beg,end);//删除[beg,end)区间的数据,返回下一个数据的位置.erase(pos);//删除pos位置的数据,返回下一个数据的位置以上操作与deque容器相同,不同的是,list支持remove操作:
.remove(elem);//删除容器中所有与elem值匹配的元素#include#includeusing namespace std; void PrintList(const list& lst) { for (list::const_iterator it = lst.begin(); it != lst.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; } cout << endl; } int main() { listL1(10, 1); PrintList(L1); L1.remove(1); PrintList(L1); return 0; }
只支持存取首位:
.front();//返回第一个元素.back();//返回最后一个元素list本质是链表,不是用连续性空间存储数据
//验证迭代器是不支持随机访问的 listL1(10, 1); list::iterator it = L1.begin(); it++;//可以运行 //it += 1;//会报错
如何验证容器支持的迭代器:
it++;//支持向前it--;//双向迭代器it += 1;//支持随机访问.reverse();//反转链表.sort();//链表排序不能使用sort(L1.begin(), L1.end());
sort默认升序排列,如果要降序,要写仿函数,sort参数为函数名
#include#includeusing namespace std; void PrintList(const list& lst) { for (list::const_iterator it = lst.begin(); it != lst.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; } cout << endl; } bool myCompare(int v1,int v2) { //降序,就让第一个数大于第二个数 return v1 > v2; } int main() { //验证迭代器是不支持随机访问的 listL1; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { L1.push_back(i); } PrintList(L1); L1.reverse(); PrintList(L1); L1.sort();//默认从小到大 PrintList(L1); L1.sort(myCompare); PrintList(L1); return 0; }
以Person为例,有姓名、年龄、身高等属性
排序规则:按照年龄进行升序,如果年龄相同,按照身高进行降序
高级排序方法:
>和<,分别为降序和升序#include#include#includeusing namespace std; class Person { public: Person(string name, int age, int height) { this->m_name = name; this->m_age = age; this->m_height = height; } string m_name; int m_age; int m_height; }; //制定排序规则 bool myCompare(Person& p1, Person& p2) { //按照年龄升序 if (p1.m_age == p2.m_age) //年龄相同,按照身高降序 return p1.m_height > p2.m_height; else return p1.m_age < p2.m_age; } int main() { listl; //准备数据 Person p1("A", 10, 100); Person p2("B", 17, 90); Person p3("C", 15, 190); Person p4("D", 15, 150); Person p5("E", 15, 90); //插入数据 l.push_back(p1); l.push_back(p2); l.push_back(p3); l.push_back(p4); l.push_back(p5); for (list::iterator it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); it++) { cout << (*it).m_name << " " << (*it).m_age << " " << (*it).m_height << endl; } l.sort(myCompare); for (list::iterator it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); it++) { cout << (*it).m_name << " " << (*it).m_age << " " << (*it).m_height << endl; } return 0; } Copyright © 2023 leiyu.cn. All Rights Reserved. 磊宇云计算 版权所有 许可证编号:B1-20233142/B2-20230630 山东磊宇云计算有限公司 鲁ICP备2020045424号
磊宇云计算致力于以最 “绿色节能” 的方式,让每一位上云的客户成为全球绿色节能和降低碳排放的贡献者