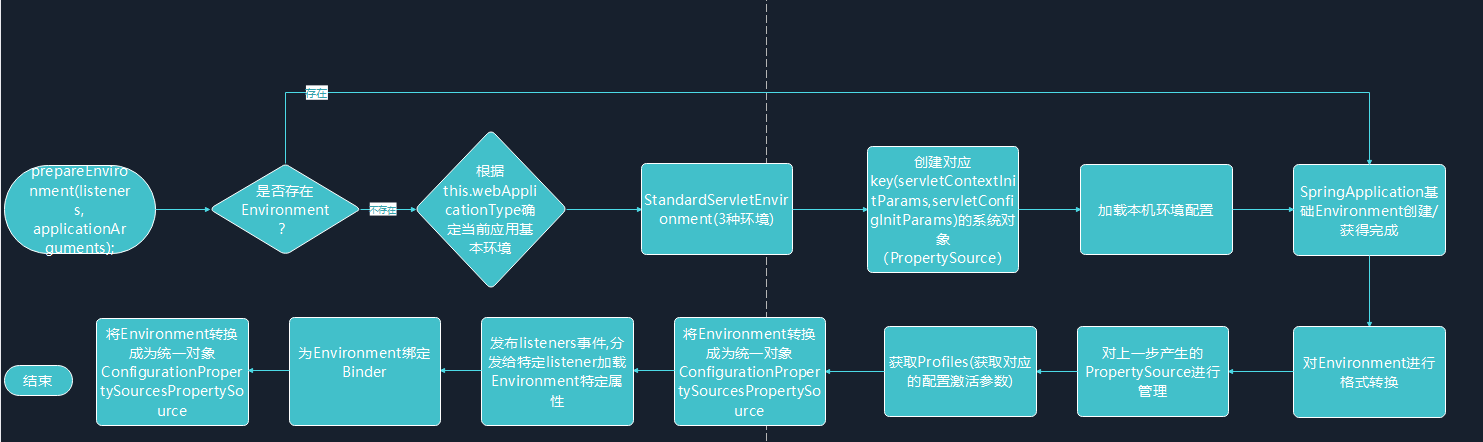
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String...args){ } //记录任务耗时 StopWatch stopWatch=new StopWatch(); stopWatch.start(); ConfigurableApplicationContext context=null; CollectionexceptionReporters=new ArrayList<>(); configureHeadlessProperty(); //加载并实例化META-INF/spring.factories下面的SpringApplicationRunListener所对应的class集合 SpringApplicationRunListenerslisteners=getRunListeners(args); //根据参数决定加载某些listener,并且start listeners.starting(); //SpringApplication的参数封装 ApplicationArguments applicationArguments=new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); //这里便是重点 ConfigurableEnvironment environment=prepareEnvironment(listeners,applicationArguments); //下面还有,这里不讲......
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments){ // 获取或者根据一定条件创建Environment对象,这里返回的是StandardServletEnvironment() ConfigurableEnvironment environment=getOrCreateEnvironment(); //为Environment设置了系统参数以及一些相关的PropertySource configureEnvironment(environment,applicationArguments.getSourceArgs()); //对PropertySource转化为ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment); //事件发布(具体逻辑在listeners.start里面讲过了) listeners.environmentPrepared(environment); //为environment与Binder建立联系(至于为什么,我也不知道,留个????) bindToSpringApplication(environment); //是否为自定义的环境 if(!this.isCustomEnvironment){ //如果不是自定义环境,则会对environment进行格式转换 environment=new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass()); } ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment); return environment; }
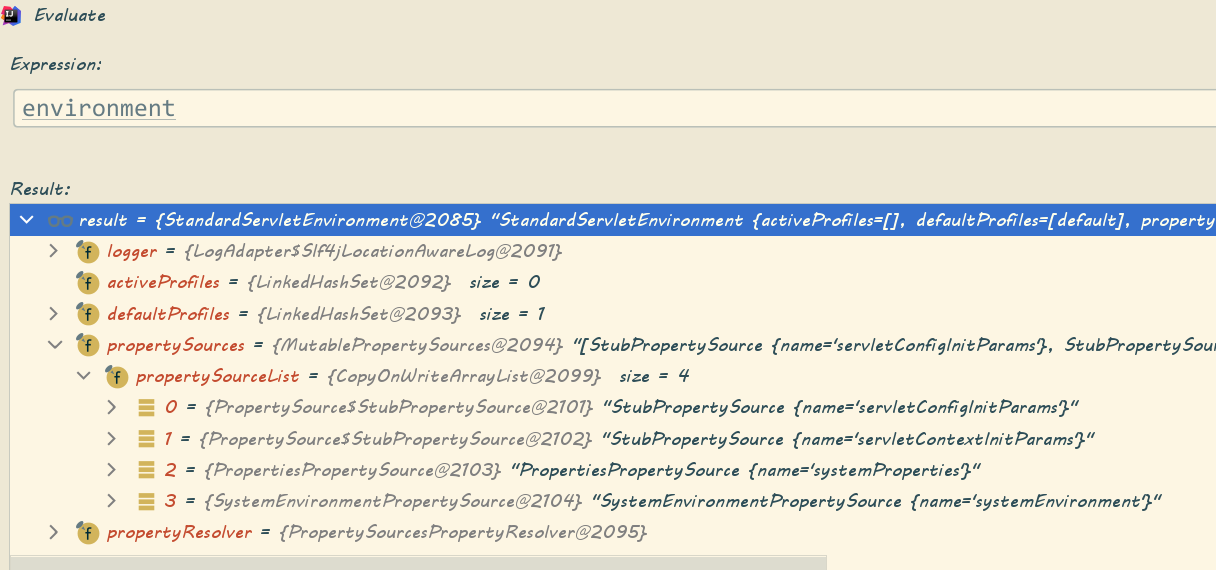
private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment(){ //是否存在环境 if(this.environment!=null){ return this.environment; } //根据当前应用类型,加载不同的Environment对象 //至于怎么获取当前应用类型,在构造SpringApplication时讲了 switch(this.webApplicationType){ //servlet环境 case SERVLET: return new StandardServletEnvironment(); //响应式环境 case REACTIVE: return new StandardReactiveWebEnvironment(); //非web环境 default: return new StandardEnvironment(); } } • StandardServletEnvironment#customizePropertySources(),为Environment配置几个键值对象 public class StandardServletEnvironment extends StandardEnvironment implements ConfigurableWebEnvironment { @Override protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) { //往MutablePropertySources添加了名为servletContextInitParams, // servletConfigInitParams的StubPropertySource对象 propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)); propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)); if (JndiLocatorDelegate.isDefaultJndiEnvironmentAvailable()) { propertySources.addLast(new JndiPropertySource(JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)); } //通过父类添加了名为systemEnvironment的PropertiesPropertySource对象 //通过父类添加了名为systemProperties的SystemEnvironmentPropertySource对象 super.customizePropertySources(propertySources); }
protectedvoidconfigureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,String[]args){ //ConversionService:懒汉式线程安全单例模式,管理了一系列bean的转化 if(this.addConversionService){ ConversionService conversionService=ApplicationConversionService.getSharedInstance(); environment.setConversionService((ConfigurableConversionService)conversionService); } //对 PropertySource进行管理(主要是系统属性的配置),后面会讲 configurePropertySources(environment,args); //这里主要对系统环境的配置,决定激活什么配置文件 configureProfiles(environment,args); }
protected void configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,String[]args){ //获取当前系统environment的PropertySources MutablePropertySources sources=environment.getPropertySources(); //检测是否存在默认配置,如果有则添加到PropertySources中(低优先级) if(this.defaultProperties!=null&&!this.defaultProperties.isEmpty()){ sources.addLast(new MapPropertySource("",this.defdefaultPropertiesaultProperties)); } //从命令行参数读取参数,并且加入到PropertySources中 if(this.addCommandLineProperties&&args.length>0){ String name=CommandLinePropertySource.COMMAND_LINE_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME; //如果原先的PropertySources存在此命令行key if(sources.contains(name)){ PropertySource source=sources.get(name); //则新建一个CompositePropertySource对象 CompositePropertySource composite=new CompositePropertySource(name); //并且添加到PropertySources composite.addPropertySource( new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource("springApplicationCommandLineArgs",args)); composite.addPropertySource(source); //然后替换掉原来的用新的对象替换掉原来的key sources.replace(name,composite); } else{ //否则直接在最前面添加命令行参数(高优先级) 如:java-jar --server.port......等参数 sources.addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args)); } } }
protected void configureProfiles(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,String[]args){ Setprofiles=new LinkedHashSet<>(this.additionalProfiles); profiles.addAll(Arrays.asList(environment.getActiveProfiles())); //往下看 environment.setActiveProfiles(StringUtils.toStringArray(profiles)); }
public void setActiveProfiles(String...profiles){ Assert.notNull(profiles,"Profile array must not be null"); if(logger.isDebugEnabled()){ logger.debug("Activating profiles "+Arrays.asList(profiles)); } synchronized (this.activeProfiles){ //清除自身的被激活的环境 this.activeProfiles.clear(); for(String profile:profiles){ //验证环境 validateProfile(profile); //确认需要激活的环境 this.activeProfiles.add(profile); } } }
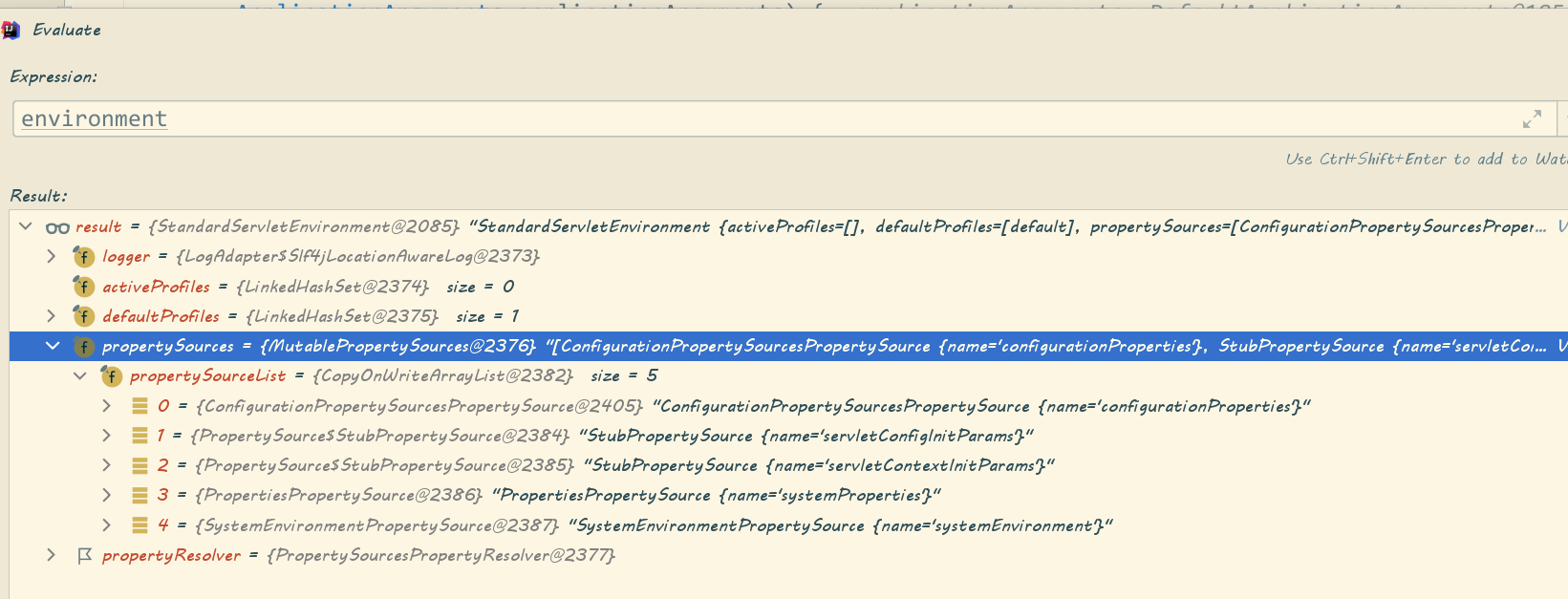
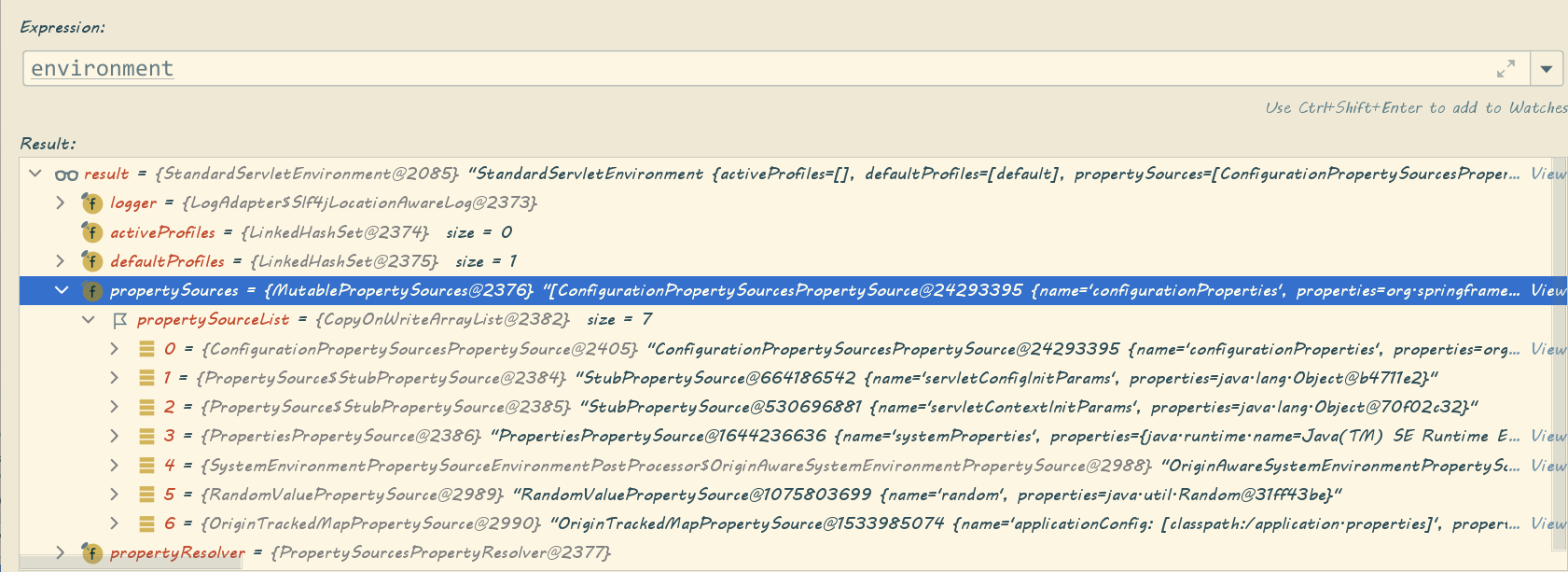
public static void attach(Environment environment){ Assert.isInstanceOf(ConfigurableEnvironment.class,environment); //获取当前environment的PropertySources MutablePropertySources sources=((ConfigurableEnvironment)environment).getPropertySources(); PropertySource attached=sources.get(ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME); if(attached!=null&&attached.getSource()!=sources){ sources.remove(ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME); attached=null; } if(attached==null){ //PropertySources转化为ConfigurationPropertySources,为后续Binder.get(this.environment)打下基础 sources.addFirst(new ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource(ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, new SpringConfigurationPropertySources(sources))); } }

protected void bindToSpringApplication(ConfigurableEnvironment environment){ try{ //先为environment建立Binder对象,为SpringApplictaion设置key Binder.get(environment).bind("spring.main",Bindable.ofInstance(this)); } catch(Exception ex){ throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot bind to SpringApplication",ex); } } Copyright © 2023 leiyu.cn. All Rights Reserved. 磊宇云计算 版权所有 许可证编号:B1-20233142/B2-20230630 山东磊宇云计算有限公司 鲁ICP备2020045424号
磊宇云计算致力于以最 “绿色节能” 的方式,让每一位上云的客户成为全球绿色节能和降低碳排放的贡献者